Attention is all you need
Paper Summary
Paper
Background
-
Until this paper came about, there was work done to use attention on text (Neural Machine Translation) and images (Show Attend and Tell)
-
The authors propose a new architecture based on attention mechanism that is parallelizable and trains fast called the Transformer.
-
In recurrent networks, current hidden state is a function of previous state and the current input. This sequential relationship makes parallelizing difficult to achieve which can be cumbersome at longer sequences.
-
Attention mechanism on the other hand model dependencies without regard to distance in input or output sequences.
-
Transformer architecture moves away from recurrence and relies entirely on attention to learn global dependencies between input and output.
-
In transformer, learning dependencies between distant positions is a constant operation with the tradeoff being reduced effective resolution since attention weights are averaged. However, this is alleviated with the use of Multi-head attention blocks.
-
Self attention is relating different positions of a single sequence to compute it’s representation.
Architecture
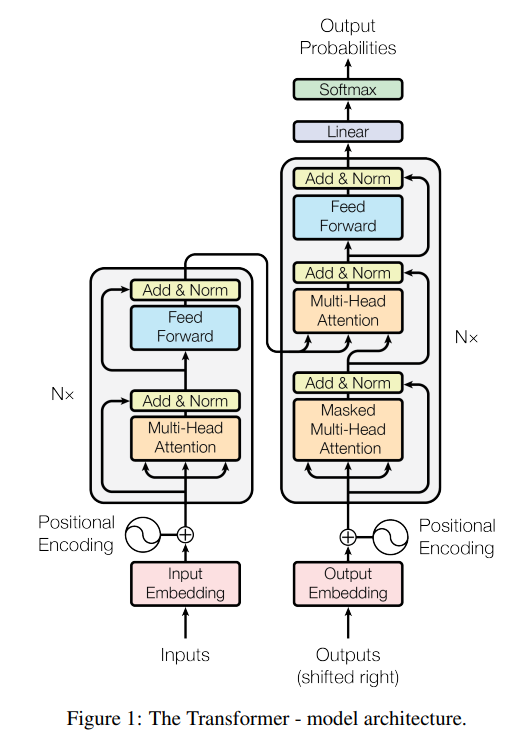
An autoregressive (AR) based encoder-decoder model is proposed. The input sequence representations are encoded by the encoder into a continous sequence representations. The decoder uses the encoder output to generate model’s output sequences one element at a time. Since the model is AR, it uses the previously generated symbols as additional input when generating the subsequent symbol.
Encoder
- Encoder contains a stack of 6 identical layers where each layer has two sub layers:
- Multi-head self-attention mechanism
- FC feed forward network
- A residual connection is used around each sub-layer followed by a normalization layer.
- The embedding as well all the sub-layers produce dmodel = 512 dimensional output.
Decoder
- Decoder contains a stack of 6 identical layer where each layer has the two-sub layers from above as well as a multi-head attention layer that operates on the encoder output.
- Residual connections are used in a similar fashion to the encoder.
- Masking is employed in the self-attention layer in the decoder to prevent positions to attend to future ones i.e. to ensure the current position cannot take a peep at the future positions.
Attention
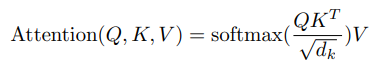
-
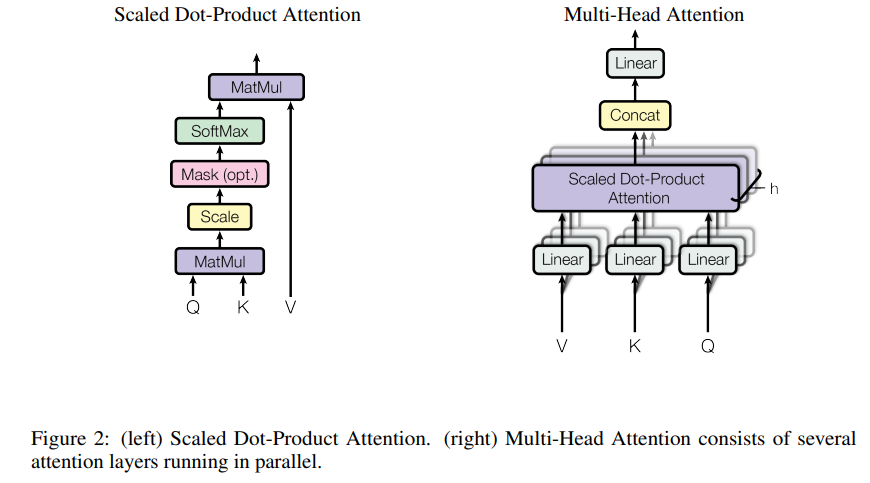
Attention function is described in the paper as mapping a query and a set of key-value pairs to an output, where the query, keys, values, and output are all vectors. The output is computed as a weighted sum of the values, where the weight assigned to each value is computed by a compatibility function of the query with the corresponding key.
-
You can think of query as the current word, the model is trying to translate or decode and based on that, attention tells you where in the input you should attend to, to find the most relevant information. Key and value are from the input. In self-attention, Q, K, V are all from the input.
-
Queries and keys are of same dimension dk and values are of dimension dv.
Multi-Head attention
- Rather than performing a single attention block with a 512 dimensional query, key and values, they linearly project queries, keys and values h times each with different learned projections to dq, dk, dv dimensions where dq, dk, dv = 512/h.
- Attention functions are computed parallelly on each of these projected versions resulting in h different dv dimensional value outputs that are then concatenated together, and projected to a dmodel = 512 dimensional output.
- This mechanism enables the model to jointly attend to information from different representational spaces at different positions.
- Since dimension of each head is lower than a model dimension, computational cost is comparable to that of a single attention block.
Layers
-
Encoder-decoder attention layers - Queries come from previous decoder layer while keys and values come from the encoder output. Therefore, every position in the decoder can attend over all positions in the input sequence.
-
Self-attention layers - Queries, keys and values all come from output of the previous layer in encoder or decoder depending on where it is implemented. Each position in the encoder (or decoder) can attend over all positions from previous layer of encoder (or decoder). In decoder, you want to attend from all positions in the decoder until the position in consideration (including). This is achieved by setting all illegal connections to infinity which would be turned to zero by a softmax layer.
-
The feedforward layers are applied identically to each position separately. The same parameters are used across positions but they differ across layers. Input and output dimensions are dmodel = 512.
Positional embeddings
- Due to the absence of recurrence or convolutions, to encode the sequence order, positional embeddings are used which are added to input embeddings in encoder and decoder.
- They have the same dimension as input embedding i.e. dmodel = 512.
- Sine and cosine functions of different frequencies are used to learn absolute/relative order in the sequence and this also allows the model to operate on sequences longer than what was encountered while training.
Self-attention benefits
- Path length between long range dependencies - Self-attention layer connects all positions with a constant number of sequential operations O(1) whereas recurrent layers requires O(n) sequential operations.
- When they say O(1) I think they mean during decoding a word, the different attention heads in the multi-head attention block look at the relation between the word being decoded and different input word encodings. For example, in “The animal didn’t cross the street because it was too tired.”, one attention head might be looking at “animal” while decoding “it” and another might be looking at “street” while decoding “it”. This happens in parallel so it’s O(1). In RNNs, this happens sequentially, i.e. you have go through each word.
- Computation complexity - Self-attention layers are faster than recurrent layers when sequence length n is smaller than representation dimensionality.
- Self-attention also leads to more interpretable models.
References
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: